The usage of Business Intelligence tools has seen an exponential increase with the advent of the BigData era. Every organization wants to carry out an insightful analysis of its data and make data-backed business decisions to improve its working efficiency. Tables are used to store this huge amount of data in a meaningful way. Using the concept of rows and columns, Tables have simplified searching, identifying, and understanding of data. Every person working with data encounters Tables and works with them.
In this article, you will get a clear understanding of Highlight Tables and Tableau. You will also learn how to set up Tableau Highlight Tables through a step-by-step tutorial.
Table of Contents
What is the Tableau Highlight Tables?
The name Tableau Highlight Tables is self-explanatory. Just like how we like to highlight important text in a document, Tableau Highlight tables help highlight the important information and values in a table. You can either highlight them conditionally or apply various color schemes.
Looking for the best ETL tools to connect your data sources? Rest assured, Hevo’s no-code platform helps streamline your ETL process. Try Hevo and equip your team to:
- Integrate data from 150+ sources(60+ free sources).
- Utilize drag-and-drop and custom Python script features to transform your data.
- Risk management and security framework for cloud-based systems with SOC2 Compliance.
Try Hevo and discover why 2000+ customers have chosen Hevo over tools like AWS DMS to upgrade to a modern data stack.
Get Started with Hevo for FreeWhen and How to Use Highlight Tables?
You can use a highlight table to highlight important values in a text table. Using highlight tables allows the user to easily distinguish the higher measures from the lower measures.
You should take a note of the following pointers before making Highlight Tables:
- Always make measures that are significantly different from each other.
- Avoid using the same colors for similar measures.
- Use a divergent color palette only when your data crosses a meaningful threshold.
- Avoid using multiple colors. This may confuse the user.
How To Read Highlight Tables?
Highlight tables are used to highlight data in a text table. They use color to speed up the process of identifying the most important numbers within a range of values. These tables also include rows and columns to represent various dimensions. Comprehending all this information might help you in reading Highlight Tables.
What is the Importance of Tableau Highlight Tables?
- Tableau Highlight Tables are great for comparing values within a column or row.
- Tableau Highlight Tables allow users to perform conditional formatting to a view of a normal table using different color schemes.
- Tableau will help you automatically apply a color scheme as an endless or stepped array of colors ranging from highest to lowest.
- You can also use Tableau Highlight Tables to highlight similar categorical data with color.
- Tableau Highlight Tables are extremely useful as they help users quickly spot the most important and interesting data in a table.
What Type of Analysis Do Highlight Tables Support?
Highlight tables are text tables that have been enhanced with the use of color to show high and low values. Assume you have a financial spreadsheet that tracks revenue, loss, profit, net income, gross income, costs, and sales. For each labeled data point, you can use a different color on the measured value. If you only want to highlight declines, you can use one color for negative examples (ex. red). To distinguish between positive and negative outcomes, use a contrasting color (ex. black).
Prerequisites
- Working knowledge of Tableau
- A Tableau Developer Account
- Tableau installed at your workstation
What are the steps to Set up a Tableau Highlight Table?
Step 1: Open Tableau and log into your account.
Step 2: In the navigation pane on the left, click on Connect. A list of connection options is displayed. Select the data source that you want to work with. In this tutorial, a sample superstore Dataset is taken for your understanding. The Tableau Highlight Table created with this Dataset will have the regions as the row attributes and segments (There are three kinds of customer segments in this Dataset) as the column attributes.
Step 3: Once you’ve chosen your sample Dataset, a new window opens up. On the left side of the menu, the Data tab lets you explore the data in your dataset. Choose the attribute that you want to use for your columns. Drag and drop it into the column bar on the worksheet. Look at the image below- it shows the Superstore data and the Segment data attribute has been dragged into the column bar.
Step 4: Now, drag the required data attribute onto the Row bar. In this example, Region data is being added to the row bar. You can also add subcategories into the row bar by dragging and dropping it. You can see in the image that there are three segments in the column namely Consumer, Corporate, and Home Office. There are 4 different regions in the rows. The subcategories are different products listed in each region. What you now see is a normal table. Let’s add some color schemes to it.
Step 5: Drag a measurable attribute onto the Color icon. The below image shows the profit attributed dragged onto the Color icon. Tableau aggregates the profits region-wise for different accessories across different segments. The color will indicate the amount of profit. You can see the color coding on the right side of the worksheet with the least profit measure of $5300 and the highest as $12790.
You can also make more changes to your Tableau Highlight Table depending on your use case. You can edit the colors, add more attributes to the Tableau Highlight Table and explore your data.
Examples of Highlight Tables
Take a look at the following highlight table:
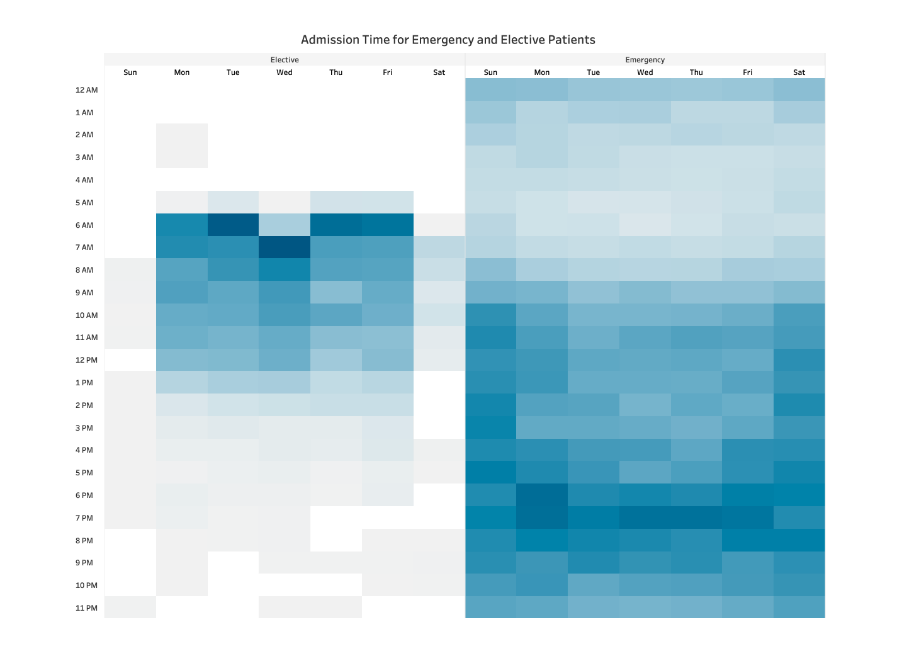
The highlighted table above examines the number of patients admitted to a hospital and their respective wait times. The darker the color, the greater the number of patients in the waiting room at that time.
- The information is distributed evenly. Viewers can see when there are more patients waiting and when the waiting room is empty.
- Elective and emergency wait times are separated into two tables but are coloured the same.
What is Tableau?
Tableau is a Business Intelligence Software as a Service (Saas) platform that helps various organizations analyze their data and create attractive visualizations like charts, graphs, maps, etc. With the help of Tableau, you can understand your data better, derive insights with ease, and make data-driven business decisions.
Tableau also empowers you to build interactive Dashboards, thereby giving you a complete overview of your data. Using these Dashboards, employees from cross-functional departments can collaborate effectively and seamlessly. Tableau boasts its use anywhere feature because it is available across different platforms such as desktop, tablet, mobile and online. Learn more about Tableau and its usage from their official documentation.
What are the Key Features of Tableau?
Tableau is powerful and widely used by a lot of organizations. Let’s look at some of its key features:
- Multiple Data Sources
- A Wide Range of Visualizations
- Data Filtering
- Dynamic and Interactive Dashboards
- Easy Collaboration
1) Multiple Data Sources
Since all operations performed in Tableau depend on data, it supports integration with a large number of storage applications, Relational, In-house & Cloud databases, and numerous other sources such as:
- Microsoft Excel
- CSV files
- MS SQL Server
- Oracle
- IBM DB2
- Google BigQuery
- Windows Azure
- ODBC/JDBC,etc
You can use these integrations to move your data into Tableau and analyze your data with numerous tools & create informative visualizations.
2) A Wide Range of Visualizations
As discussed, Tableau provides a wide range of tools to its users and enables them to create different types of data visualizations using their data. You can easily create the simplest to most complex visualizations using Tableau. Let’s look at some of its visualizations:
- Scatter plot
- Line plot
- Pie Chart
- Bar Chart
- Bullet Chart
- Highlight Tables
- Gantt Chart
- Boxplot, etc.
Using Tableau’s Map features you can view your data on a geographical map. So, it is highly useful for organizations having multiple outlets or centers across various countries and who want to analyze the performance of each of them.
3) Data Filtering
Tableau also houses an interesting feature that allows users to not only filter data from a single source but also supports data filtering across multiple data sources. The condition for data filtering across multiple data sources is that the data must have similar dimensions. This automatically results in the required changes being made to all worksheets with the same data sources using the same set of filters.
4) Dynamic and Interactive Dashboards
With the power of Tableau, you can build dynamic and interactive Dashboards where you can manipulate your visualizations, etc. Tableau also allows its users to format their Reports and Dashboards and make them compatible with mobile devices. With Tableau, users can create various customized mobile layouts for their Reports or Dashboards for their devices.
5) Easy Collaboration
It’s important for everyone to understand their data and make informed decisions which are critical to success and that’s why Tableau is built for collaboration. Using Tableau, team members can share data, make follow-up queries with fellow peers, and share visualizations with anyone who can gain value from them. From web editing and authoring to data source recommendations, Tableau gives its users the ability to work and understand the data they need. You can easily publish your Dashboard to Tableau Server or Tableau Online within seconds and as a result, everyone in your organization can see your insights, ask various questions, and make the right decisions.
Conclusion
Perceiving a visual form of data (charts, diagrams, etc ) is simpler than looking at thousands of data rows. Tableau Highlight Tables not only allow you to see your data in the form of a table but also color co-ordinate or highlight the important pieces of information that can help you save a lot of time that would otherwise be spent manually trying to identify crucial information and trends. After reading this article you should be able to set up Tableau Highlight Tables and work with them.
Carrying out an insightful analysis through visualizations such as Highlight Tables can be challenging especially when you need data from multiple data sources that Tableau does not support, and this is where Hevo comes into the picture. Hevo is a No-code Data Pipeline and has awesome 100+ pre-built integrations that you can choose from. Hevo can help you integrate your data from numerous sources and load them into a destination to analyze real-time data with a BI tool such as Tableau. It will make your life easier and data migration hassle-free. It is user-friendly, reliable, and secure. Check out the pricing details here. Try Hevo by signing up for a 14-day free trial and see the difference!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the use of the highlight table in Tableau?
Used for visualizing data values with color to identify patterns and trends.
2. Can you highlight specific rows in Tableau?
Achieved through conditional formatting or filters.
3. How do you highlight top 3 values in Tableau?
Create a rank field, apply a filter for the top 3, and use conditional formatting to visually distinguish these values.

