It is a common practice for most businesses today to rely on data-driven decision-making. Businesses collect a large volume of data and leverage it to perform an in-depth analysis of their customers and products, allowing them to plan future Growth, Product, and Marketing strategies accordingly. In this era of Big Data, businesses are, however, generating huge volumes of Unstructured Data.
Unstructured Data Definition can include various forms of data storage, including audio, video, text data, sensor data, imaging, etc. Until recently, businesses found it hard to analyze Unstructured Data because of the immense resources required to go through it manually.
Table of Contents
What is Unstructured Data Definition?
- Unstructured Data (also called Qualitative Data) refers to data that does not have any predefined structure. Typically, Unstructured Data is text-heavy, such as Social Media conversations and open-ended survey responses, but it also includes audio, videos, and images.
- The high volumes of Unstructured Data can be attributed to the increasing use of digital services and applications. Estimates show that 80-90% of data generated by companies is unstructured, and it continues to grow at a high rate each year.

Examples
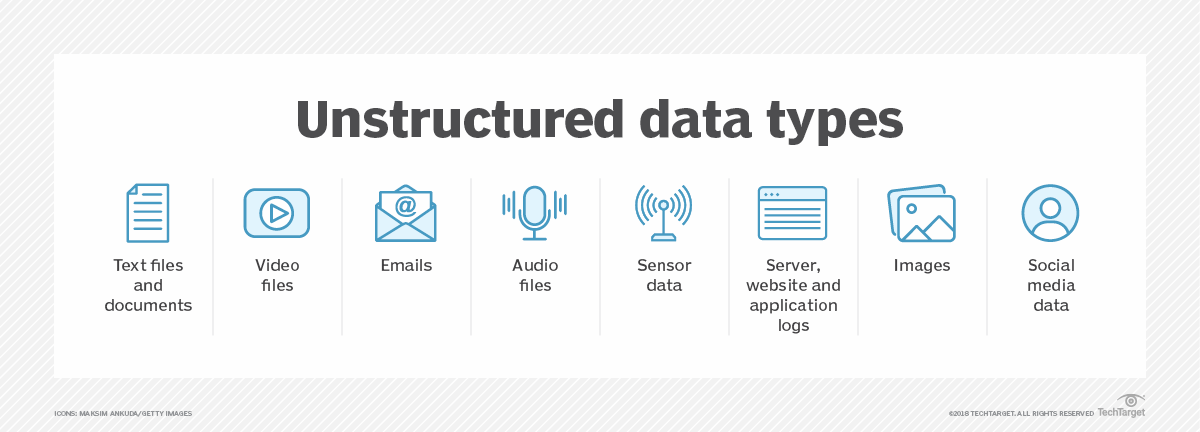
Any data that does not have a recognizable structure is Unstructured Data. The most common examples of Unstructured Data are as follows:
- Emails: The body of the Email does not follow a predefined format.
- Photos.
- Text files.
- Video files.
- Web Pages and Blog Posts.
- Audio files.
- Social Media sites.
- Call Center Transcripts / Recordings.
- Presentations.
- Open-ended Survey Responses.
Advantages of Using Unstructured Data Definition
Unstructured Data is considered to be an untapped resource for most modern businesses. If appropriately managed, Unstructured Data can give numerous insights that can help businesses make informed data-driven decisions.
This means that organizations should look for ways to collect and process Unstructured Data properly to help them make critical business decisions and prosper even in highly competitive environments.
Machine learning technology has made it much easier for companies to analyze Unstructured Data quickly and accurately.
These companies use technological advancements like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand Unstructured Data. This saves companies from having to do repetitive tasks like sifting through the data manually.
Businesses that analyze their Unstructured Data can benefit in the following ways:
- Improved Customer Experience
- Identify Market Gaps
- Listen to Customers
Disadvantages of Using Unstructured Data Definition
The following are the disadvantages associated with the use of Unstructured Data Definition:
- Storage: Most businesses are generating huge volumes of Unstructured Data, running up to terabytes in size. Handling such data is a complex process as more resources are required for storage and computation.
- Complex Indexing: Indexing Unstructured Data is a difficult and error-prone process due to an undefined structure and no pre-defined attributes. As a result, analysis of Unstructured Data sometimes does produce very accurate insights.
- Processing: Most Data Analysis tools were designed for processing Structured Data. This means that businesses have to go through many steps to transform Unstructured Data into a form suitable for analysis.
Analyzing Unstructured Data Definition
Initially, there weren’t many reliable techniques for the analysis of Unstructured Data Definition, and hence, it had to be done manually. Today, there are a wide variety of Data Analysis tools that use robust Machine Learning algorithms for the analysis of Unstructured Data Definition. Users can perform an analysis of Unstructured Data by implementing the following steps:
- Step 1: Determining the End Goal
- Step 2: Collecting Relevant Data
- Step 3: Cleaning Data
- Step 4: Implementing the Necessary Technology
Step 1: Determining the End Goal
First, you should define a set of clear goals. The goals should help you understand what insights you need to derive from the Unstructured Data Definition.
Step 2: Collecting Relevant Data
There are numerous data sources available from where you can extract or collect the necessary data. However, you may need to focus on just one channel, such as Social Media posts, Customer Reviews, Surveys, etc. So collect relevant data based on your area of focus.
Step 3: Cleaning Data
This will make it easier for the Data Analysis tool to process the Unstructured Data Definition. You also have to remove noise and outliers from the data and reduce it into smaller and manageable pieces.
Step 4: Implementing the Necessary Technology
Other than the implementation of Data Analysis tools, a lot of effort is required to extract insights from Unstructured Data. You will need data storage tools such as NoSQL databases and Data Visualization tools like Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Google Data Studio, etc.
Conclusion
- This article provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Unstructured Data Definition, its advantages, and disadvantages, along with the steps involved in Analyzing Unstructured Data.
- The data to be analyzed, however, has to be imported from numerous sources.
- Setting up a data pipeline from all your data sources would require immense engineering bandwidth and resources in developing and maintaining the pipeline and ensuring high data accuracy. Businesses can instead use automated data integration platforms like Hevo

