This article talks about Snowflake UI and provides information about its Database, Warehouse, Worksheet, and History pages. In addition to that, It also talks about other UI help and user menus, and browser requirements. It also explains how you can Access Documentation, Support, Downloads, and Context-sensitive help regarding Snowflake UI.
Snowflake is one of the popular Data warehouse solutions that work on the cloud infrastructure. It is designed with the help of advanced SQL systems. It is highly scalable in nature and has the functionality of parallel computing. It is based on AWS and Azure platforms.
The Ease of use nature is complemented by the proper interface known as the Snowflake UI.
Table of Contents
What is Snowflake?

Snowflake is a fully managed warehousing service that allows customers to connect, load, analyze, and securely share data while providing nearly unlimited scalability for parallel operations. Common use cases include data lakes, data engineering, data application development, data science, and secure data use.
Snowflake’s architecture is unique in that it naturally separates computation and storage. This approach can provide users and data workloads with virtual access to a single copy of data without sacrificing speed. Snowflake allows you to run your data solution across multiple locations and the cloud for a consistent experience. Snowflake makes this possible by abstracting the complexity of the underlying cloud infrastructure.
The virtual Warehouse concept of Snowflake is applied to Amazon EC2 clusters to provide necessary processing power
each virtual warehouse contains an MPPEC2 computing cluster with many nodes that provides faster data analysis. Snowflake retains the on-demand scaling of these virtual warehouses and the ability to pause when not in use.
Snowflake users can connect with thousands of other users using the Snowflake Data Marketplace. This Marketplace also provides access to shared datasets and data services.
Snowflake pricing demystified – try our free, interactive calculator now!
Key Features of Snowflake
Some of the advantages of employing Snowflake:
Caching Results: A notable feature of Snowflake is the caching of results at different levels. This means that the data results will last for 24 hours after the query is executed. So if the same query is run again by any user in your account. Results are already available. This is useful when comparing queries before and after changes.
Unique architecture: A fusion of traditional shared disks and Shared Nothing databases. Similar to the shared disk architecture, Snowflakes relies on a central repository of data accessible from all nodes in the platform. On the other hand, in an MPP computing cluster (massively parallel processing), each node stores a part of the whole data individually. Like a SharedNothing database. This allows users to enjoy the simplicity of the SharedDisk architecture and the power and benefits of the SharedNothing database.
Data Sharing: Snowflake provides secure data sharing capabilities that allow you to share items from one database in one account to another without creating duplicates. This guarantees more storage space and less storage work. Snowflakes’ metadata memory makes accessing data easier and faster. Therefore, Snowflake creates a network of data providers and consumers that enables many use cases. For those who do not have an account, Snowflake offers the option to create a leader account. This is a low-cost option that gives consumers free access to shared data.
Processing Semi-Structured Data: To process semi-structured data, Snowflake’s architecture uses a schema to read the data type Variants. It stores both structured and semi-structured data to the same destination. When the data is loaded, Snowflake parses the data and automatically extracts the attributes. Later this data will be saved in column format.
Minimal administrative work: Snowflake is provided as a data warehouse as a service and requires minimal administrative work. Scalability capabilities minimize DBA and IT team involvement. No software or hardware installation is required.
Scalability: Snowflake’s architecture scales compute and storage resources separately. This allows users to scale up resources when large amounts of data need to be uploaded at short time intervals and scale down the resources again without impacting the service. To minimize management, Snowflake has introduced automatic scaling. This automatically starts and stops the cluster during unpredictable resource processing.
Getting Objects: It’s humans to make mistakes. The UNDROP command is a solution to the mistakes that occur when you drop the wrong table and split the data. With traditional data recovery, recovery and backup can take a lot of time. You can use this command to instantly restore snowflakes as long as you are in the restore window.
Zero-copy cloning: When cloning an existing database, the use of traditional data warehousing services is hectic because you need to provide a completely new environment to upload your data. This is not feasible as it may add additional costs to the customer. Snowflake’s Zerocopy feature is the solution to this problem. This feature allows you to clone immediately without making a new copy that saves storage. Modify the metadata store clone while referencing the original data file on the backend. The time travel feature of cloning data from past points in time makes this warehouse one of the best warehouses.
ETL cost visibility without leaving Snowflake.
What is Snowflake UI?
You can create and manage all Snowflake objects, including virtual warehouses, databases, and all database objects by logging in to Snowflake’s web-based graphical user interface. It allows the users to run additional queries, view past queries, load data into a table in limited quantities, and perform DDL/DML operations on the same. You can also change your Snowflake user password and set other settings such as your email address through the user interface.
It allows you to perform administrative tasks like adding and managing users only if you have a required administrator role. Learn more about administrator tasks.
It is divided into 6 main pages namely:
Database Page

This page displays information about the databases you have created or have access to. The tasks you can perform on this page (if you have the appropriate permissions) include:
- Create, duplicate, or delete a database.
- you can change the ownership details of the database by assigning it to other users
- You can also click the database name to view and perform tasks for objects in the database.
Warehouse Page

This page displays information about the virtual warehouses you have created or have access to. The tasks you can perform on this page (if you have the appropriate permissions) include:
- Create or delete a warehouse.
- Pause or resume data warehouse.
- Configure the warehouse.
- Transfer ownership of the warehouse to another role.
Worksheet Page
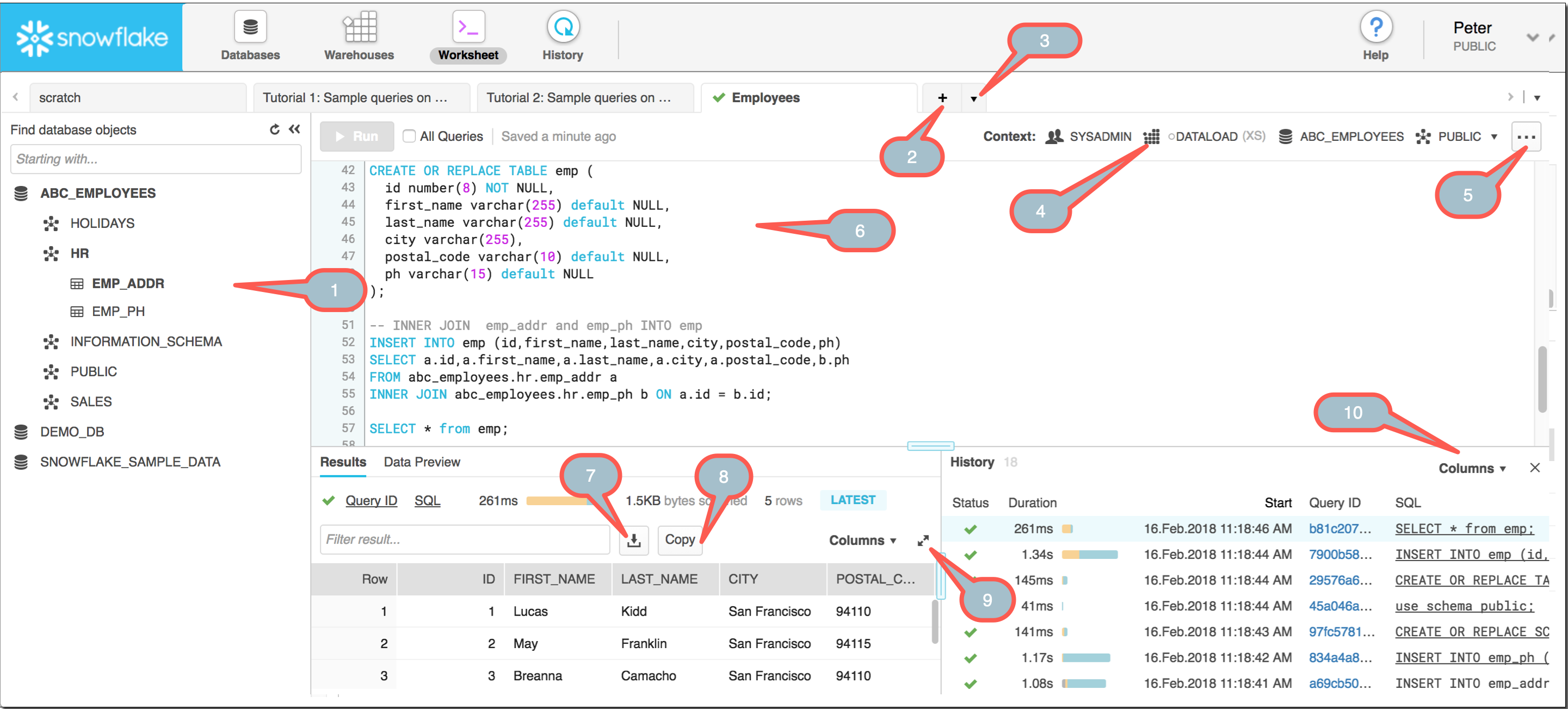
SQL queries can be run, DDL and DML operations can be performed with ease using the Worksheet page of the Snowflake UI. This page also displays the results side by side of the operation as soon as it completes execution.
The page also provides many functionalities, a few functions that can be performed on the page are:
- Loading SQL script files, executing queries, and other DDL / DML operations on worksheets.
- Opens a simultaneous worksheet. Each worksheet has its own individual session.
- Save the worksheet and reopen it.
- You can refresh the browser page without losing the work, switch privileges on the worksheet or Log out of Snowflake.
- Resize the current warehouse to increase or decrease the computational resources used to execute queries and DML statements.
After logging out of Snowflake, all active queries will no longer be executed.
Exports the result of the selected instruction (if the result is still available).
Learn more about Query Worksheets / DML / DDL.
History Page
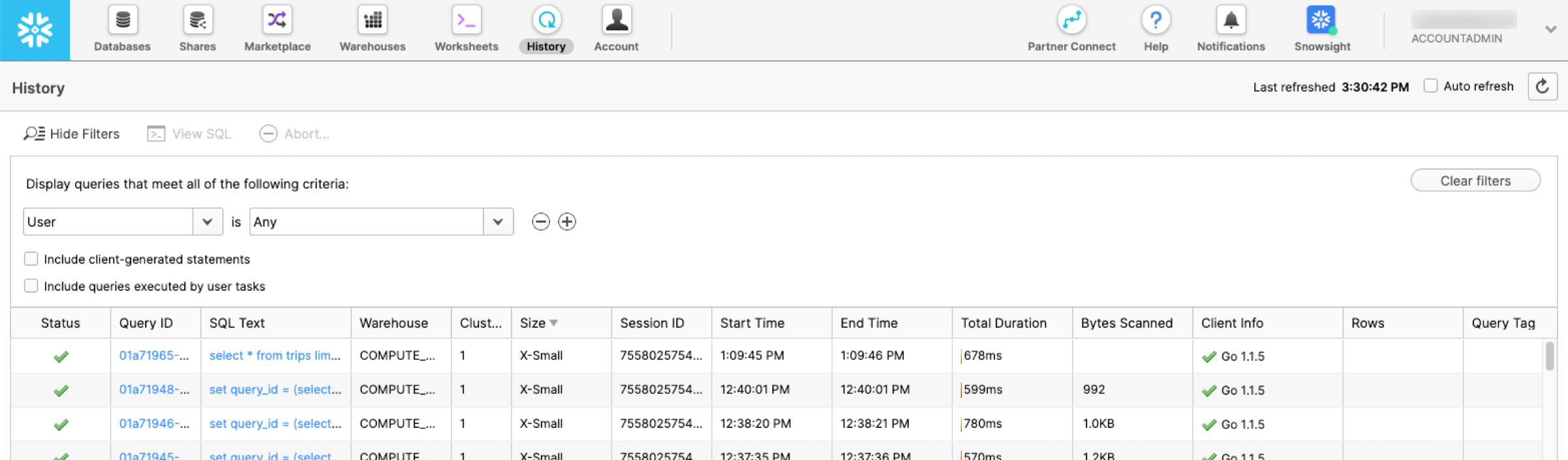
On this page, you can view and explore the details of queries that have been executed in the last 14 days. A History list of queries that were executed even by SnowSQL and other SQL clients is also displayed on this page. This page allows you to perform various different tasks such as:
- The queries shown on the page can be filtered based on requirements
- Scroll the list of displayed queries.
- Displays query details, including the results of the query. Query results are available 24 hours a day. This limit cannot be adjusted.
- Change the displayed column.
- The page allows verifying the SQL text that is being used, checking the Status of queries, verifying the ID, checking the warehouse, and last but not least verifying start and end times for performance metrics by Clicking one of the column headings.
Help Menu
This menu can be accessed by clicking on the help icon in the upper right corner of the Snowflake UI.
The drop-down menu provides you with many options select one of the following to perform a function:
- open a new browser/tab to open the snowflake document.
- Open a new Browser/tab to access the support portal.
- The snowflake client can also be downloaded by opening the dialog box.
- the dialog box offers further options such as:
- Download the ODBC driver and the SnowSQL which is a Snowflake CLI client.
- Display the information regarding the downloads of the Snowflake JDBC driver, Snowflake connector for Spark, driver details for Node.js, and other python components.
- Also displays the context-sensitive help relevant to the current page in the help area.
User Menu
You can access this menu by clicking on the dropdown in the upper right, next to your login name.
- If you have proper privileges assigned, you can change the password and security roles for the session.
- The dropdown menu also offers various functions that you can perform a few being:
- If additional languages are enabled for your account you can switch languages for the user’s session.
- If you have administrator rights you can set up an email address to receive notifications.
- You can close the current session, exit the snowflake web interface or log out from the session
- you can find the information regarding the organization linked to the Snowflake account, the edition of snowflake being used, and the region where the snowflake account is being used.
Browser Requirements
Accessing Documentation, Support, Downloads, and Context-sensitive Help
To access these resources at any time, click the icon on the Help tab in the upper right corner. From the drop-down menu, select one of the following actions:
- View Snowflake Document: Opens the document in a new tab/window.
- Access the Community
- Open the Snowflake Support Portal / Community in a new tab/window.
- A community is a place where you can freely browse the articles and discussions on the site. However, you will need to log in to the portal with your Snowflake community credentials to submit cases and participate in discussions. These credentials are different/unique from the Snowflake user’s credentials.
- Download: Displays a dialog box where you can perform the following operations.
- you can download the client software provided by snowflake Command Line Client (SnowSQL) ODBC Driver (for Platforms)
- Displays distribution information for the following client software. Provided by Snowflake: Spark v2.0 and later connectors
- JDBC driver,
- Python (and related components) connector
- Node.js driver
- Show help window
- Show context- Confidential help for the current page. It Includes:
- Description on page
- . A task that can be completed on-page
- step-by-step description to complete a specific task.
Conclusion
This article gives a comprehensive guide in detail.
Snowflake is a trusted data warehouse that a lot of companies use and store data as it provides many benefits but transferring data into it is a hectic task. The Automated data pipeline helps in solving this issue and this is where Hevo comes into the picture.
Share your experience of learning in the comments section below.




