Storing data in an organized way makes it easy for everyone to access and process the data. Google Sheets is one of the most popular tools for data storage and analysis. It allows its users to store data online for free.
With Google Sheets, one can store data in cells and organize it in the form of columns. It is a great tool for data storage for both individuals and organizations. The good thing is that you can store data of any size in Google Sheets.
However, when the data becomes too large, searching for a specific data within Google Sheets may become an issue. However, the Google Sheets SQL makes it easy for you. With Google Sheets SQL function, you can perform database-style searching on your spreadsheet.
This way, you can perform searches quickly and easily.
In this article, you will be seeing how to perform searches on Google Sheets using the Google Sheets Query function.
Quickly transfer Google Sheets data to any data warehouse—Redshift, BigQuery, Snowflake, and more—without writing a single line of code. Ensure real-time, analysis-ready data for streamlined reporting and insights.
- No-code data migration in minutes
- Automated real-time data syncing
- Seamlessly connect to top data warehouses
- Instantly load Google Sheets data for faster insights
Transform your Google Sheets into actionable business intelligence with ease.
Get Started with Hevo for FreeTable of Contents
How to Add Data to your Spreadsheet
As you can see on your screen, the Google Spreadsheet is made up of cells. If you begin to type, what you type will be populated into the selected cell, usually the top left cell. You can select any cell that you need and type something in it.
Once you are done typing, press the ENTER key to save the data. You will be moved to the beginning of the next row. You can also press the TAB key to save the data and move to the right in the same row. Other than the mouse, you can use the arrow keys on your keyboard to move from one cell to another within the spreadsheet.
In the next section, you will learn about Google Sheets SQL function in detail.
Understanding the Query Functions
To give instructions in SQL fashion in Google Sheets, the QUERY function is used. The format of the function is:
=QUERY(data, query, [headers])
In Google Sheets SQL, the QUERY function has three parameters where only two are required. The parameters are:
data– Range of cells containing the data.query– SQL-like query.headers– Number of rows that contain header information.
How to Use the Google Sheets Query Function
The Google Sheets SQL function is a very important function to Google Sheets users. It supports the use of database-type commands to manipulate Google Sheets data. It is a very powerful and versatile function.
If you have used SQL, you will find the Google Sheets Query function easy to use. In the next few sections, you will be seeing how to use Google Sheets SQL function to perform various tasks on Google Sheets.
The integration of SQL Google Sheets allows for seamless transition between spreadsheet data manipulation and SQL-based data querying, facilitating a more comprehensive approach to data analysis and reporting.
You can read more about Google Sheets SQL function from here.
Create a Table
We will be using the following data:
We need to join the data into a single table so that we can refer and access it easily in our Google Sheets Query function.
Do this:
Step 1: Select the whole table.
Step 2: Click “Data” from the menu and choose “Named ranges”.
Step 3: A new window will pop on the right side of your spreadsheet. Type “countries” in the first input box. You will have named the table so that you can use it easily. Click “Done”.
Good!
The table is now set up.
We will be writing our pseudo-SQL code inside the Google Sheets Query function as shown below:
=QUERY(countries,"your SQL code goes here",1)SELECT all the Data
You can use the SELECT * query to retrieve all the columns of your table.
Type the following query on cell F1:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT *",1)Hit the ENTER key.
The query will return the entire table:
SELECT Specific Columns
We can use the Google Sheets SQL function to select only specific columns. We want to select only the “Country” and “Rank” columns from the table.
Modify your QUERY function to read as follows:
=query(countries,"select B, D",1)This returns the following:
WHERE Clause
The WHERE clause helps you specify a condition that must be met and it’s good for filtering data. It should come after the SELECT clause. We want to see the names of countries that generate a revenue of more than $20,000.
Modify your QUERY command in cell F1 to the following:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A, B WHERE B > 20000",1)The query will return the following output:
Only three countries satisfied our search criteria.
Let’s see the list of countries that are in Asia:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A, C WHERE C = 'Asia' ",1)The query returns the following result:
ORDER BY Clause
You can use the ORDER BY clause to sort your data. You have to specify the columns to be sorted and the order of sorting, whether ascending or descending. It should come after SELECT and ORDER BY clauses:
Let’s sort our countries by revenue, from largest to smallest (descending order):
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A, B ORDER BY B DESC",1)The query returns the following result:
To sort the data in ascending order, replace the DESC with ASC in the command.
LIMIT Clause
You can use the LIMIT clause to restrict the number of results that are returned. It should come after the SELECT, WHERE, and ORDER BY clauses.
Let’s modify our previous command to return the top 5 countries in terms of revenue:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A, B ORDER BY B DESC LIMIT 5",1)The query returns the following result:
COUNT Command
The COUNT command can help you to count data. Let’s say that you want to count the number of countries per continent.
Modify the command on cell F1 to the following:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT C, count(A) GROUP BY C",1)The query returns the following result:
The number of countries per continent has been shown.
AND and OR Clauses
These two clauses can help you add multiple search criteria to your formula. For example, we can use the AND clause to search for countries that are located in Europe and generate a revenue of more than $20,000.
The following query demonstrates this:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A, B, C WHERE (B > 20000 AND C='Europe')",1)This returns the following result:
We can use the OR clause to get the list of countries that belong to either Europe or Asia:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT A WHERE (C = 'Europe' OR C='Asia')",1)The query returns the following result:
Arithmetic Functions
You can perform standard arithmetic operations on numeric columns. The following query demonstrates this:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT B, C, (D / 7162119434) * 100",1)The query returns the following output:
Aggregate Function
In Aggregate Function, you use other functions in your calculations. For example, min, max, etc.
The following query will calculate, minimum, maximum and average populations in your dataset.
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT max(D), min(D), avg(D)",1)The query returns the following result:
Group By Clause
The Group By clause is used with aggregate functions to leverage data in groups. You an use the following code:
=QUERY(countries,"SELECT C, count(B) GROUP BY C",1)The query returns the following result:
Working with Columns and Conditions
To refer to individual columns in Google Sheets SQL, the following query can be used:
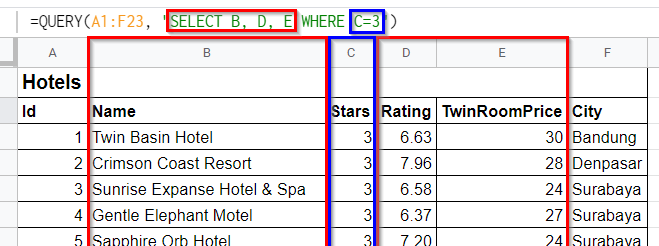
=QUERY(A1:F23, "SELECT B, D, E WHERE C=3")
Instead of using column names from your table, you can use the column letters provided by Google Sheets. In this example query given above, the column Name is located in column B in the spreadsheet, so using SELECT B you can see that in the resulting table. Note that the columns are also separated with commas, but there is no comma after the last column you want to select.
After selecting the columns, you can add the column you want to select. In the example shows, WHERE C=3. C refers to the Stars column.
Advanced techniques
There are also a few other advanced techniques in Google Sheets SQL like :
- Adding a total row to your Query formulas
- Using dates as filters in your Query formulas
- Other data manipulation functions
Limitations of the Google Sheets Query Function
The Google Sheets Query function makes it easier for you to perform search tasks when using Google Sheets.
However, it may become complex in some cases like when you want to filter your data using different factors or select data from different sheets.
Explore our detailed guide on Google Sheets as a database and learn how to turn your spreadsheets into a powerful data solution.
Conclusion
- In this article, you’ve learnt how to use Google Sheets. You’ve also learnt how to use the Google Sheets SQL Function.
- For any information on Google Sheets HubSpot Integration, you can visit the former link.
- If you’re looking for some alternative, we recommend you to try Hevo Data, a No-code Data Pipeline that helps you transfer data from a source of your choice in a fully-automated and secure manner without having to write the code repeatedly.
- Find out how to transfer data from Google Sheets to Databricks for improved data integration and analysis.
FAQ on Google Sheets SQL
Can we use SQL in Google Sheets?
No, Google Sheets does not natively support SQL for querying and manipulating data.
Can I query in Google Sheets?
Yes, you can query data in Google Sheets using Functions, add ons and scripts.
Can Google Sheets work like a database?
Google Sheets can function similarly to a database in some respects, particularly for small-scale data management and simple data manipulation tasks.
Can I use a Web query in Google Sheets?
Yes, you can use a Web query in Google Sheets to import data from websites directly into your spreadsheet.









